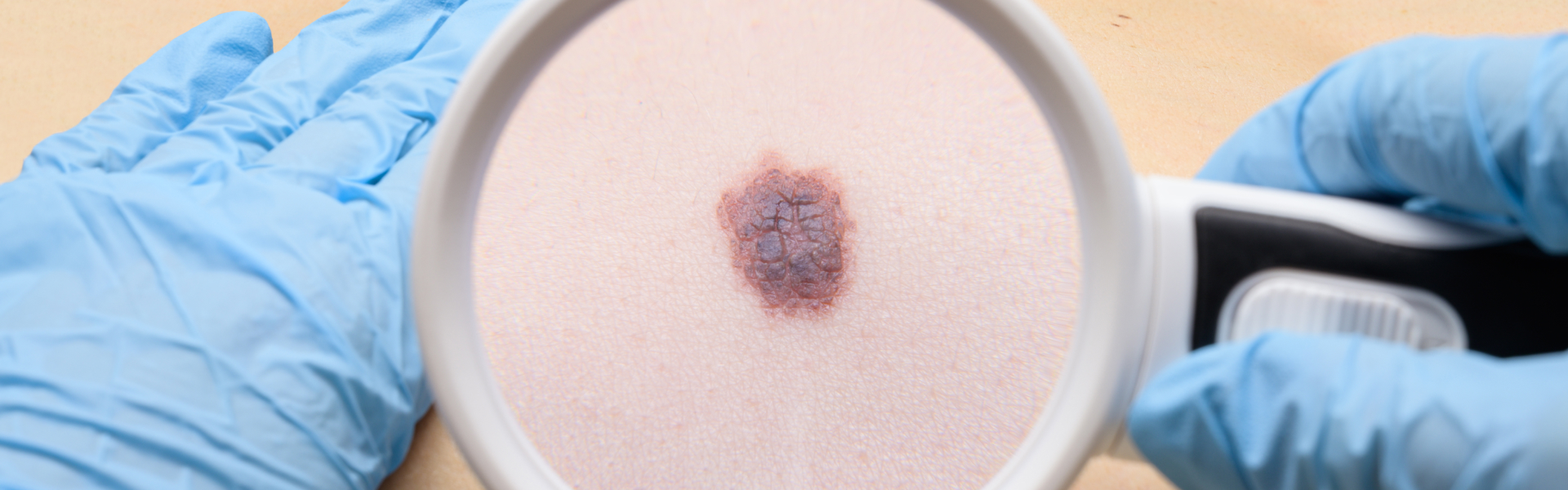
The Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Skin Cancer Program provides specialized care for patients with all stages of melanoma. We treat patients with early-stage cancerous growths through to advanced metastatic cancer. We also work with patients who may be at a higher risk of skin cancer due to family history, or who have a genetic mutation or multiple abnormal moles. We also treat other types of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell.
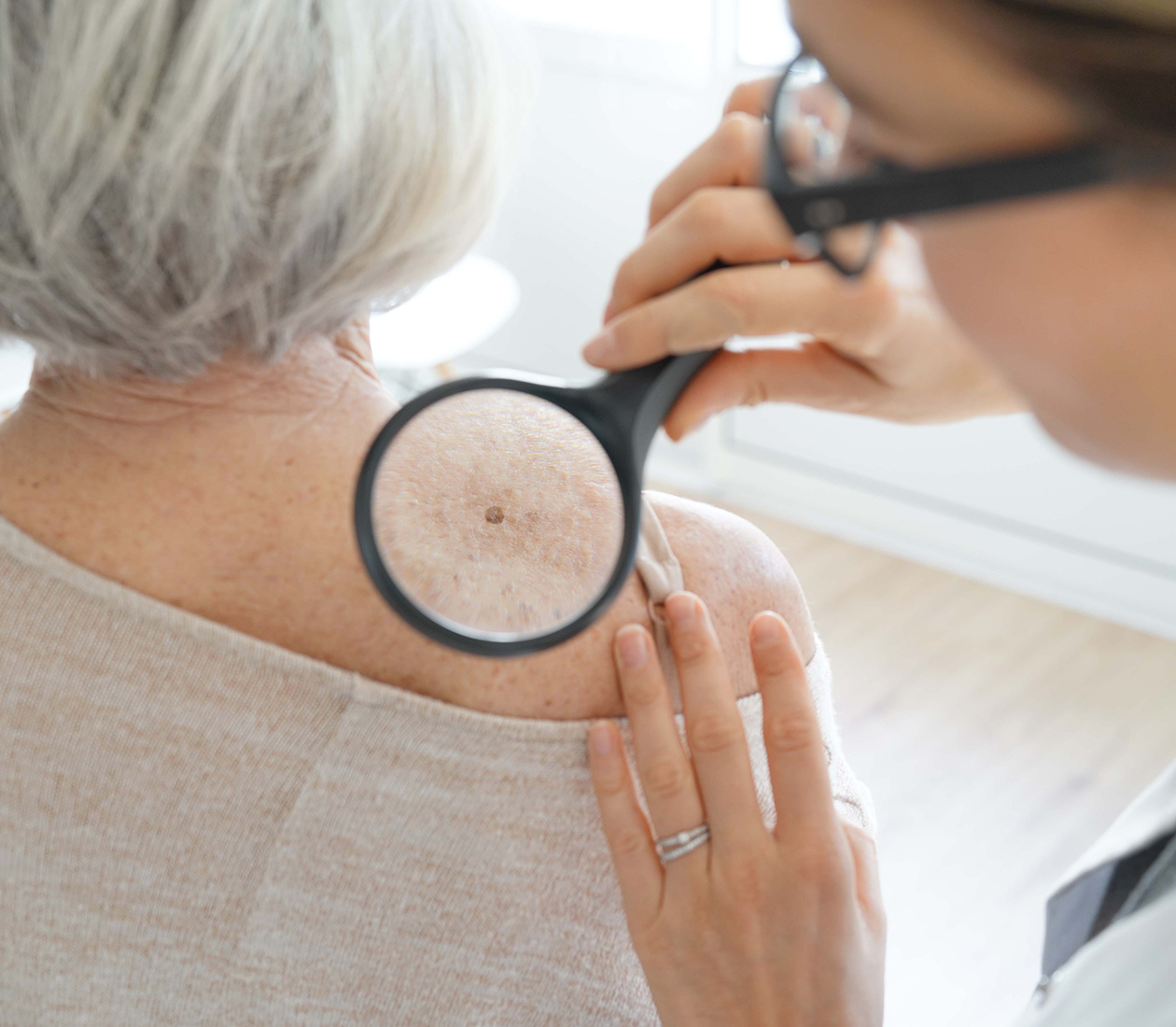
Our Skin Cancer Program provides expert care for patients with all stages of melanoma, close to home. The program brings together a team of specialties, who work collaboratively and meet regularly as a multidisciplinary tumor board to discuss each patient's case. This ensures our patients receive complete care that includes access to an array of treatment options.
Our team of specialists includes medical and surgical dermatologists, dermatopathologists, and medical, surgical and radiation oncologists.

There are three main types of skin cancer:
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer and are sometimes called “non-melanoma skin cancer.”
Melanoma is rarer than basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas but is a more aggressive type of skin cancer. If it is not treated, or it is diagnosed at a late stage, it is more likely to spread to other organs and is difficult to treat.

A change in the appearance of your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This includes a new growth appearing or a change in appearance of an existing mole or growth.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell cancer is the most common type of skin cancer. It is usually seen on skin that is exposed to the sun (including the face, hands, ears, legs, arms, mouth, or bald spots on the head). It is usually slow growing and doesn’t spread to other parts of the body. This means it is usually not life-threatening. Signs and symptoms include:
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell cancer is usually seen on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun (including the face, hands, ears, legs, arms, mouth, or bald spots on the head). It can also appear in mucus membranes and on the genitals. Signs and symptoms include:
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer which can spread to other organs. It can develop in any area, including on the eyes or internal organs. It most commonly appears on the upper back (men) and legs (women). Signs and symptoms include:
Doctors recommend the ABCDE rule to help identify skin cancers:
If you have a mole or any other skin lesion that is concerns you, always see your doctor to have it checked out.
Skin cancer is usually caused by sun exposure, especially when the skin burns or blisters. The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays damage our skin’s DNA, and abnormal cells can form which rapidly divide and cause a mass of cancer cells.
A family history of skin cancer can also increase your risk of the disease.

Your doctor will first discuss any changes you have noticed on your skin and then perform an examination of all areas of your skin, on all parts of your body.
If your doctor thinks a lesion may be suspicious, then they will perform a biopsy. This involves removing a sample of tissue and sending it to a lab to be closely examined. Your doctor with then be able to tell you whether the lesion is cancer and which type of cancer. They will also discuss the best treatment options for you.
The treatment you will receive will depend on the type of skin cancer you have and what stage it is at. In some cases, when the skin cancer is small and only on the skin’s surface, a biopsy can remove all of the cancerous tissue.
Other treatments for skin cancer include:
Cryotherapy: Using liquid nitrogen to freeze the skin cancer.
Excisional surgery: Removing the cancer/tumor and surrounding healthy skin to ensure all of the cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery: Removing the cancerous tissue only to save surrounding normal tissue. This surgery is usually given for basal cell and squamous cell cancer or if the cancer is on sensitive or important areas, including the ears, eyelids, forehead, lips, scalp, fingers or genitals.
Curettage and electrodesiccation: A sharp, looped edge instrument is used to remove cancer cells. An electric needle is then used to destroy any remaining cancerous cells. This procedure is used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers, as well as precancerous skin tumors.
Chemotherapy: Medication is given which kills cancer cells. It can be applied directly onto the skin if the cancer is only on the skin’s top layer. If the cancer has spread, chemotherapy can be given as a table or intravenously.
Immunotherapy: Drugs are given which use your own body’s immune system to kill cancer cells.
Radiation therapy: Strong beams of radiation energy are directed at the cancer to kill cancerous cells or to stop them from growing and dividing.

The Skin Cancer Program at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi consists of a multidisciplinary team of caregivers, including:

Speak with our Contact Center for assistance
Request an Appointment 800 8 2223 International Patients